Oct . 09, 2024 02:32 Back to list
plastic rain poncho factories
The Rise of Plastic Rain Poncho Factories Addressing the Demand and Environmental Impact
In recent years, the global demand for rain protection wear has surged, leading to the proliferation of factories specializing in the production of plastic rain ponchos. These lightweight, disposable garments have become ubiquitous, particularly in urban environments where sudden downpours can catch commuters off guard. But as the factories churn out an increasing number of these waterproof solutions, it is important to consider both the economic implications and the environmental challenges associated with plastic rain ponchos.
The Popularity of Plastic Rain Ponchos
The rise in popularity of plastic rain ponchos can be attributed to several factors. First, their affordability makes them accessible to a wide range of consumers. Priced often below five dollars, these ponchos are an attractive option for individuals who may not wish to invest in a more expensive, long-lasting raincoat. Secondly, their convenience is unmatched they are lightweight, easy to store, and provide immediate protection from rain, making them ideal for tourists and outdoor enthusiasts alike. As a result, factories dedicated to plastic rain poncho production have cropped up worldwide, particularly in regions with heavy rainfall or where outdoor activities are prevalent.
Economic Factors and Factory Growth
Plastic rain poncho factories contribute significantly to local economies. They create jobs in manufacturing, logistics, and distribution, providing employment opportunities for many individuals. In developing nations, these factories can spur economic growth, allowing communities to thrive around production facilities. Furthermore, the rise of e-commerce platforms has expanded the market for plastic rain ponchos, enabling factories to reach customers globally. The scale of production has increased dramatically, and companies are always looking for innovative ways to streamline operations to meet the growing demand.
However, the rapid growth of these factories also raises questions about labor practices and working conditions. In some regions, factories may prioritize output over employee welfare, prompting concerns about exploitation and inadequate safety measures. It is essential for consumers to be vigilant, advocating for ethical practices in manufacturing and supporting brands that prioritize sustainability and fair working conditions.
Environmental Impact
plastic rain poncho factories
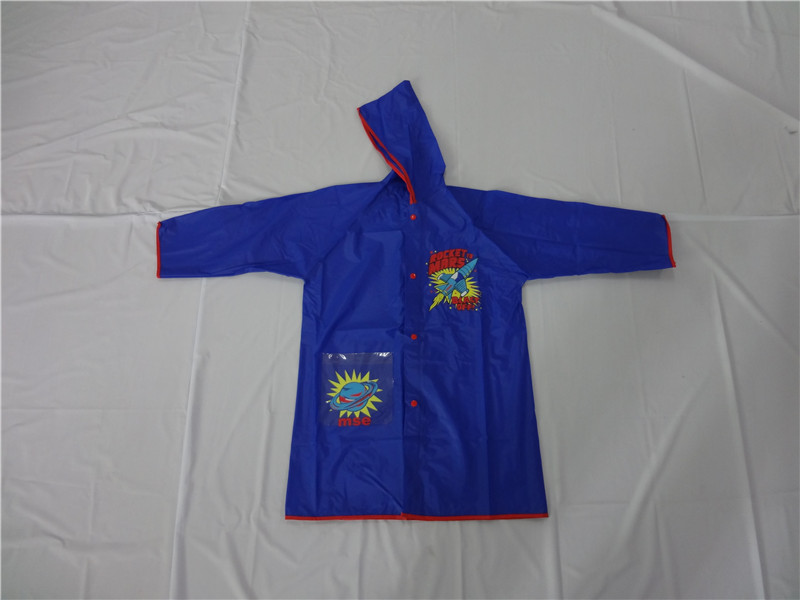

Despite their practicality, plastic rain ponchos pose significant environmental challenges. Most ponchos are made from polyethylene, a type of plastic that takes hundreds of years to decompose. The disposable nature of these products contributes to increasing plastic waste, particularly in urban areas where they are often discarded after a single use. A considerable proportion of these ponchos ends up in landfills, contributing to the global plastic crisis.
In response to growing environmental concerns, some factories are now exploring more sustainable manufacturing practices. This includes the development of biodegradable and compostable ponchos, which can decompose naturally without leaving harmful residues. Furthermore, there is a push for recycling programs that encourage consumers to return used ponchos, potentially turning waste into new products.
Consumer Awareness and Action
As awareness of environmental issues related to plastic waste grows, consumers are increasingly seeking eco-friendly alternatives. Brands that offer reusable rain ponchos or those made from recycled materials are gaining traction. This shift in consumer behavior is pushing factories to adapt and innovate, fostering a more sustainable approach to production.
Additionally, educational campaigns aimed at informing the public about the environmental impact of single-use plastics are critical. By understanding the lifecycle of plastic products, consumers can make informed choices that align with their values, ultimately driving demand for sustainable options.
Conclusion
Plastic rain poncho factories highlight a complex intersection of consumer demand, economic growth, and environmental responsibility. While these factories play a vital role in providing accessible rain protection, they also contribute to the broader challenges posed by plastic pollution. The future of the plastic rain poncho industry will depend on the ability of manufacturers to adapt to changing consumer preferences and the growing emphasis on environmental sustainability. By fostering innovation and prioritizing ethical practices, the industry can transform from one that poses a threat to the environment into one that champions sustainable solutions. As consumers become more discerning, the collective push for change could indeed pave the way for a cleaner, more sustainable future.
-
High-Quality Body Storage Bags – Reliable Manufacturer, Factory & Exporter
NewsJul.08,2025
-
High-Quality PE Cadaver Bag for Pets Reliable Manufacturer & Supplier
NewsJul.08,2025
-
Medical Depot - Leading Medical Depot Factory, Manufacturer & Exporter
NewsJul.08,2025
-
High-Quality Work Raincoat – Reliable Manufacturer & Exporter Direct from Factory
NewsJul.07,2025
-
High-Quality Pet Dead Body Bag - Reliable Manufacturer, Factory & Exporter
NewsJul.07,2025
-
High-Quality Vinly Vest Manufacturer & Exporter Custom Vinly Vest Factory
NewsJul.06,2025